画布引擎
Playground
画布引擎底层会提供一套自�己的坐标系, 主要由 Playground 驱动
Layer
P.S.
- 渲染层在底层建立了一套自己的坐标系,基于这个坐标系实现模拟滚动、缩放等��逻辑,在算viewport时候节点也需要转换到该坐标系上
- 渲染按画布被拆分成多个层 (Layer),分层设计是基于ECS的数据切割思想,不同 Layer 只监听自己想要的数据,独立渲染不干扰,Layer 可以理解为ECS的 System,即最终Entity数据消费的地方
- Layer 实现了类mobx的observer响应式动态依赖收集,数据更新会触发 autorun或render
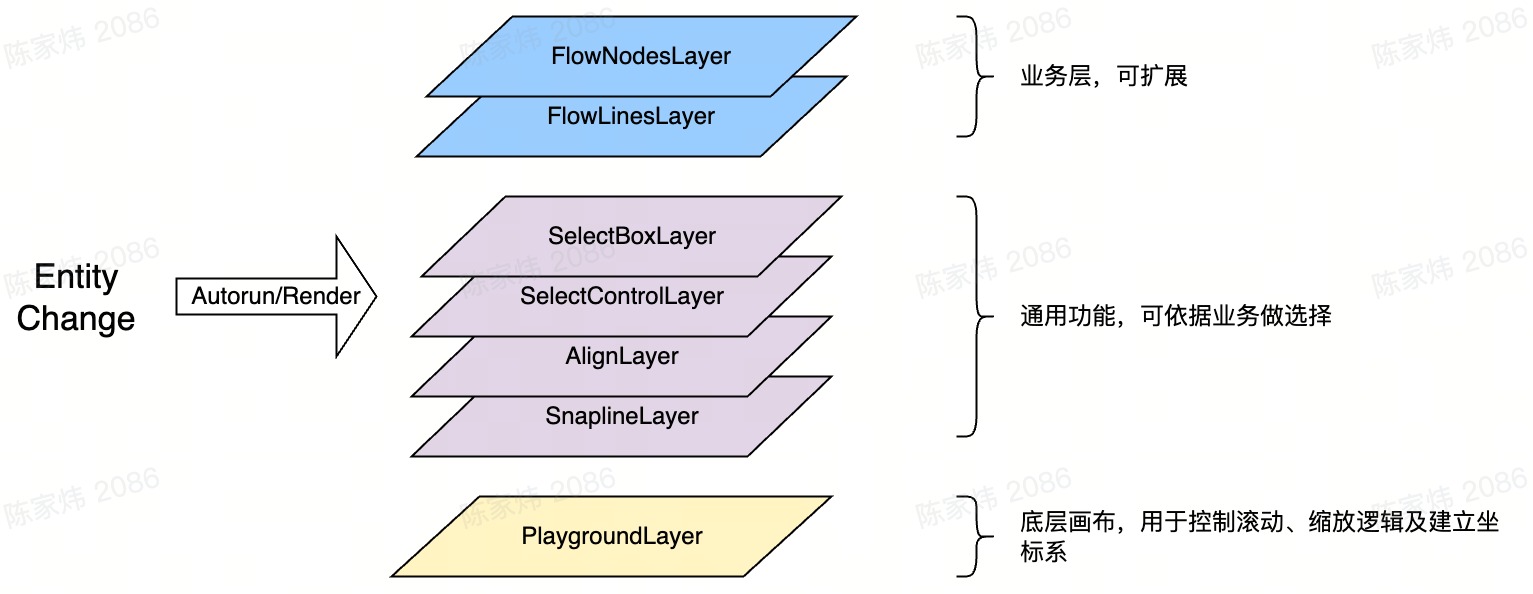
- Layer 生命周期
Layer的定位其实和 Unity 游戏引擎 提供的 MonoBehaviour 类似, Unity 游戏引擎的脚本扩展都是基于这个,可以认为是最核心的设计,底层也是基于 C# 提供的反射 (Reflection) 能力的依赖注入
- Layer 的响应式更��新
FlowNodeEntity
- 节点是一颗树, 包含子节点 (blocks) 和父亲节点, 节点采用 ECS 架构