Canvas Engine
Playground
The underlying canvas engine provides its own coordinate system, which is mainly driven by the Playground.
Layer
:::warning P.S.
- The rendering layer establishes its own coordinate system at the underlying level. Based on this coordinate system, logics such as simulated scrolling and zooming are implemented. When calculating the viewport, nodes also need to be converted to this coordinate system.
- The rendering is split into multiple layers (Layer) according to the canvas. The layered design is based on the data segmentation concept of ECS. Different Layers only listen to the data they want and render independently without interference. A Layer can be understood as an ECS System, which is the final consumption place for Entity data.
- The Layer implements observer-style reactive dynamic dependency collection similar to MobX. Data updates will trigger autorun or render. :::
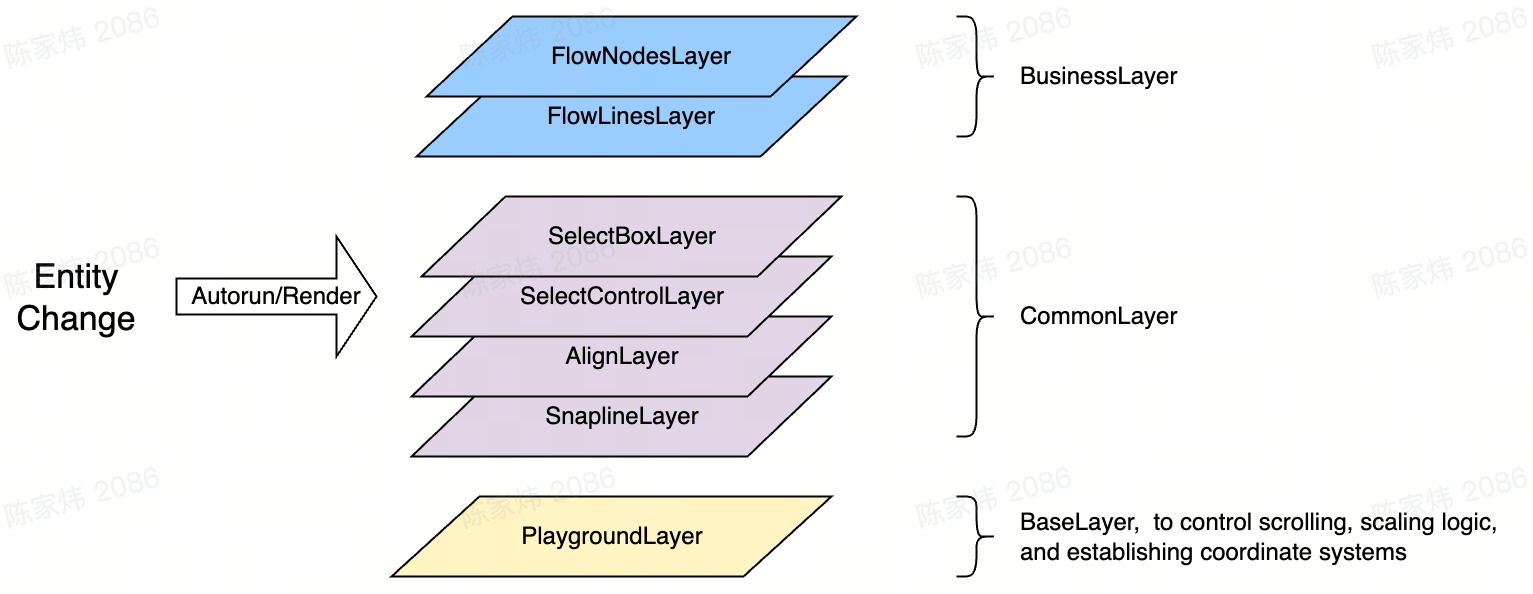
- Layer Lifecycle
The positioning of the Layer is actually similar to the MonoBehaviour provided by the Unity game engine. The script extensions of the Unity game engine are all based on this. It can be considered the core design, and the underlying layer also relies on the dependency injection capability provided by C#'s reflection.
- Reactive updates of the Layer
FlowNodeEntity
- The node is a tree, containing child nodes (blocks) and a parent node. The node uses the ECS architecture.