IOC
Why is IOC needed?
Several concepts
- Inversion of Control: Inversion of Control, a design principle in object - oriented programming, can be used to reduce the coupling between code modules. The most common way is called Dependency Injection (DI for short).
- Domain Logic: Domain Logic, also known as Business Logic, is related to specific product features.
- Aspect - Oriented Programming: AOP (Aspect - Oriented Programming). Its core design principle is to split the software system into multiple aspects (Aspect) of common logic (cross - cutting, with the meaning of penetration) and domain logic (vertical cutting). The cross - cutting part can be "consumed on demand" by all vertical - cutting parts.
Before answering this question, let's first understand aspect - oriented programming. The purpose of aspect - oriented programming is to split the granularity of domain logic into smaller parts. The cross - cutting part can be "consumed on demand" by the vertical - cutting part. The connection between the cross - cutting and vertical - cutting parts is also called weaving. And IOC plays the role of weaving and is injected into the vertical - cutting part.
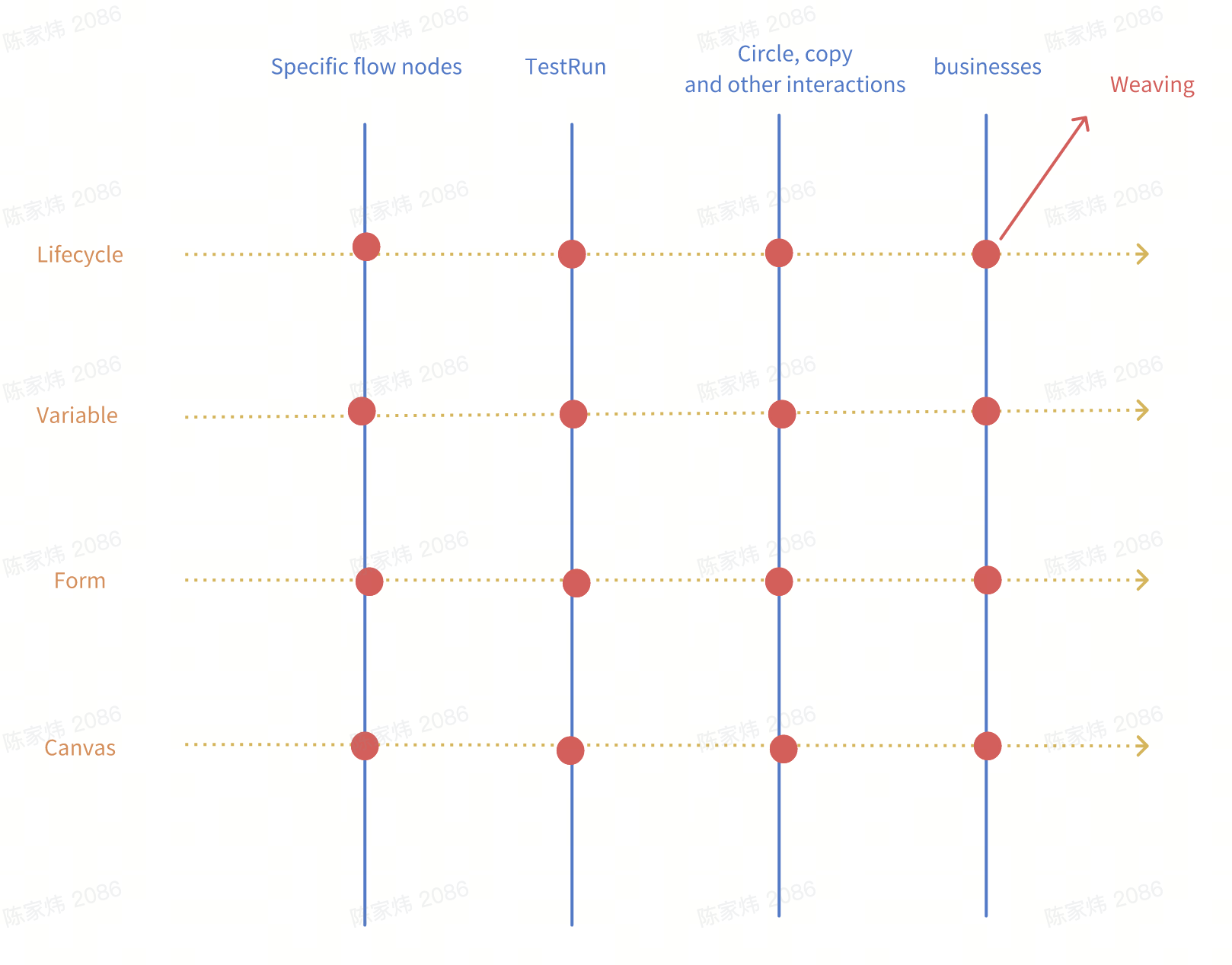
Ideal Aspect - Oriented Programming
IOC is an aspect-oriented programming technique, after the introduction, the underlying module can be exposed to the interface in the form of the external registration, which brings the following benefits:
- Implement a micro - kernel + plug - in design to achieve plug - and - play and on - demand consumption of plug - ins.
- Allow the package to be split more cleanly and achieve feature - based package splitting.